Fall Prevention Devices and Technologies for Seniors
Falls are a leading cause of injury among seniors, making it crucial to explore and utilize various fall prevention equipment and technologies designed to enhance elderly safety and prevent injuries.
These assistive devices for fall prevention can enhance safety, provide peace of mind, and help seniors maintain their independence with effective senior fall protection devices.
This article will explore a range of fall prevention devices and technologies, highlighting their features and considerations for selecting the appropriate anti-fall devices.
Importance of Fall Prevention Devices for Seniors
Fall prevention devices play a critical role in reducing the risk of falls and ensuring timely assistance when falls occur, often through advanced fall monitoring systems and caregiver alert monitors.
These devices can detect falls, alert caregivers, and provide support to prevent falls from happening in the first place using fall prevention alarms and fall alert devices.
Benefits of Fall Prevention Devices
1. Increased Safety: Provides immediate assistance and reduces the likelihood of severe injuries.
2. Peace of Mind: Offers reassurance to seniors and their families, knowing help is readily available.
3. Enhanced Independence: Enables seniors to live more independently by mitigating fall risks.
4. Timely Intervention: Ensures quick response in the event of a fall, minimizing the impact of injuries.
Types of Fall Prevention Devices and Technologies
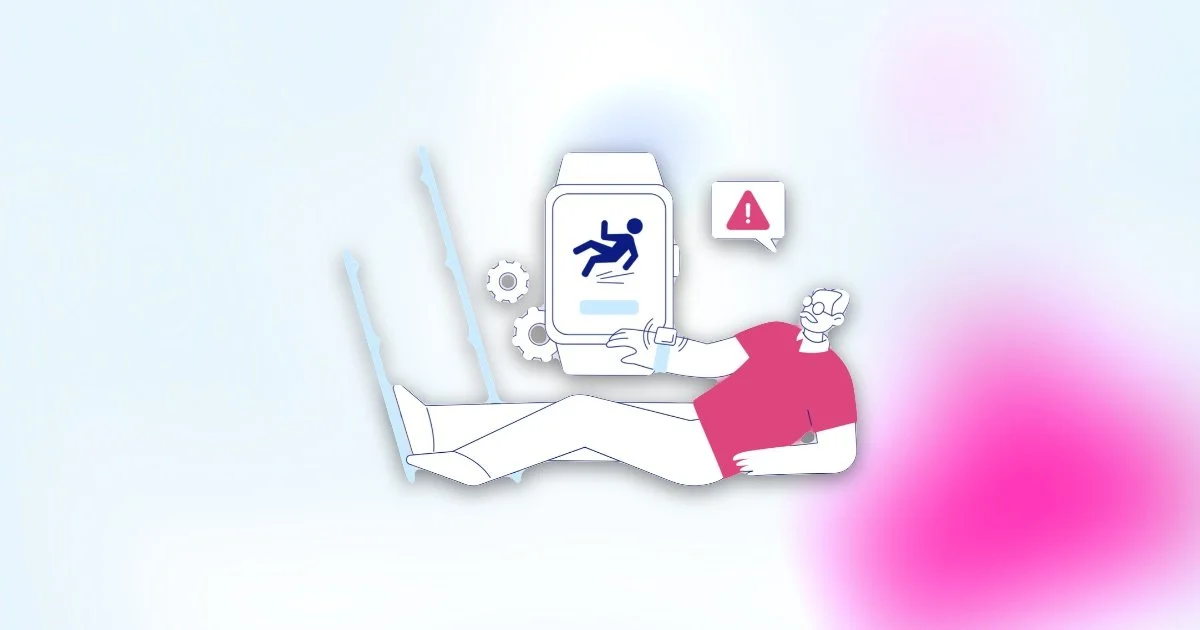
1. Wearable Sensors
Features:These wearable fall detection sensors are worn on the body and can detect falls through motion sensors. They often come with GPS tracking and emergency call buttons, making them effective fall risk bands.
Examples: Medical alert bracelets, smartwatches with fall detection, and pendant alarms.
Considerations: Look for devices with reliable fall detection algorithms, comfortable design, and long battery life. Ensure the device offers easy-to-use emergency contact features.
Wearable sensors are popular for their convenience and effectiveness in providing real-time monitoring.
These fall prevention wearable devices can automatically detect a fall and send an alert to designated contacts or emergency services through remote fall detection systems.
Advanced models even provide location tracking, which is invaluable if the user needs assistance outside the home.
2. Bed Alarms
Features: Bed alarms, bed pads, or chair pads detect when a person gets out of bed or chair and can alert caregivers to prevent falls, particularly during nighttime, making bed exit alarms and bed or chair monitors essential tools for elderly safety.
Examples: Pressure-sensitive bed pad, motion-sensor bed alarm.
Considerations: Choose alarms with adjustable sensitivity settings, loud alarms, and easy installation. Wireless options can offer greater flexibility.
Bed alarms, including a weight-activated pad and a sensor pad, are especially useful for seniors who are at higher risk of falling at night.
These bed exit alarms and monitors can provide added safety. These alarms notify caregivers if the person gets out of bed, allowing for quick intervention through caregiver alerts.
They can also be used to alert seniors if they attempt to get up, reminding them to call for assistance if needed.
3. Floor Mats
Features: These mats detect pressure changes and can alert caregivers when someone steps on them. Bedside fall mats and sensor pads are useful for monitoring movements near beds and doorways.
Examples: Pressure-sensitive floor mats, wireless floor sensors.
Considerations: Ensure mats are durable, non-slip, and easy to clean. Wireless connectivity can enhance ease of use and placement.
Floor mats are an effective way to monitor movements in critical areas, such as near beds or in hallways. Motion sensors for the elderly can also be integrated with floor mats and sensor pads.
These mats can alert caregivers when a person steps on them, providing a warning before a fall occurs with fall prevention alarms and fall alert devices.
They are particularly beneficial in nursing homes and assisted living facilities.
4. Grab Bars and Handrails
Features: These are installed in strategic locations to provide support and stability, especially in bathrooms and along staircases for enhanced bathroom safety.
Examples: Wall-mounted grab bars, fold-down handrails.
Considerations: Select bars made of sturdy, non-corrosive materials. Ensure proper installation to support the weight and prevent accidents.
Grab bars and handrails are essential for providing stability in areas where falls are most likely to occur, such as bathrooms and staircases, enhancing overall bathroom safety.
These devices offer a firm support system, making it easier for seniors to move safely, acting as effective balance aids.
5. Non-Slip Mats and Flooring
Features: These mats and flooring solutions provide additional traction to prevent slips and falls.
Examples: Non-slip bath mats, adhesive stair treads, slip-resistant flooring.
Considerations: Choose materials that are durable, easy to clean, and provide a strong grip.
Non-slip mats and flooring are simple yet effective ways to reduce fall risks.
Placing non-slip mats in bathrooms, kitchens, and other high-risk areas can prevent slips caused by wet or slippery surfaces.
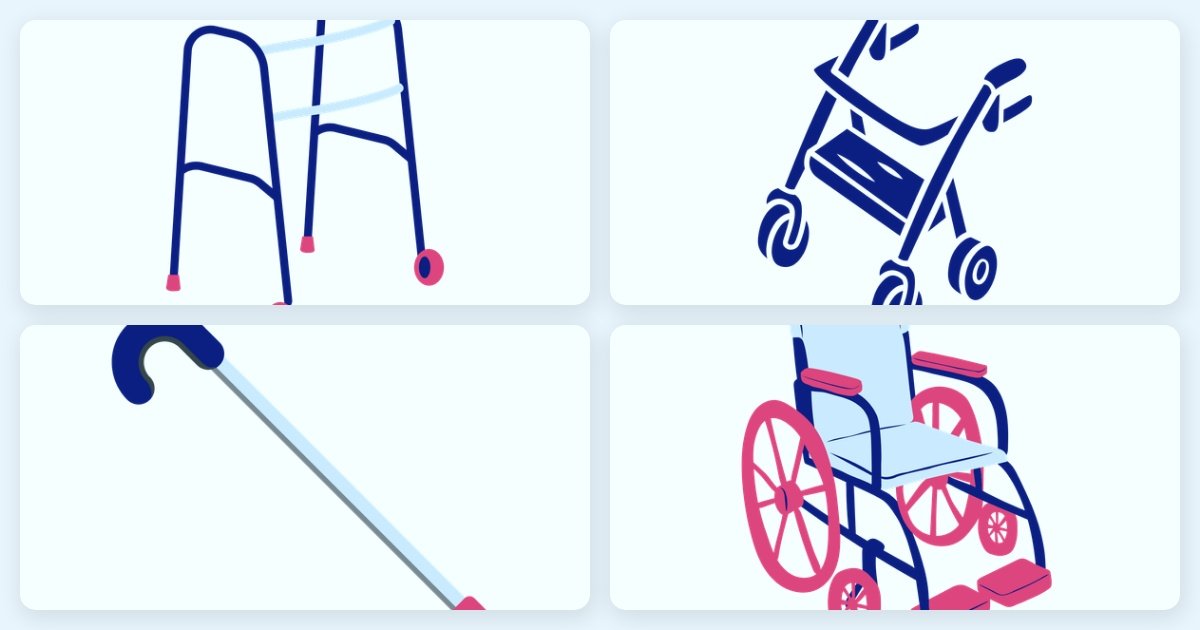
6. Canes and Walkers
Features: Mobility aids that offer support and stability during walking.
Examples: Adjustable canes, rollator walkers with seats.
Considerations: Ensure proper height adjustment and comfortable handles. Walkers with seats and storage can add convenience.
Canes and walkers are vital mobility aids that help seniors maintain balance and stability while walking, functioning as essential gait trainers and balance aids.
They are available in various designs, including those with built-in seats for rest breaks and storage compartments for convenience.
7. Personal Emergency Response Systems (PERS)
Features: These systems include wearable devices with a button to press in an emergency, connecting the user to a call center through call buttons or nurse call buttons.
Examples: In-home base units with wearable pendants, mobile PERS devices with GPS.
Considerations: Evaluate the range of the device, response time of the monitoring service, and ease of use. Mobile units with GPS can be beneficial for active seniors.
PERS devices provide a direct link to emergency services at the touch of a call button, or nurse call button.
These systems are ideal for seniors who live alone, ensuring that help is always available when needed.
Mobile PERS devices with GPS tracking are particularly useful for active seniors who enjoy outdoor activities.
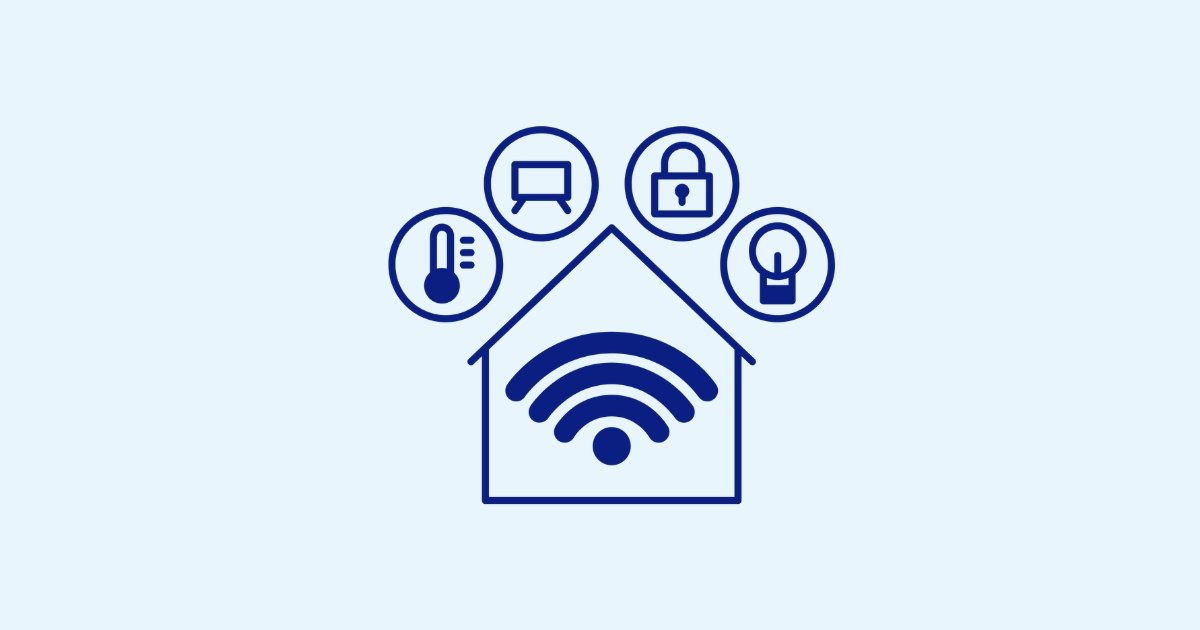
8. Smart Home Technology
Features: Integrates various home automation systems to enhance safety, such as smart lighting, motion sensors for elderly, and automated alerts.
Examples: Smart lights that turn on with motion, voice-activated assistants, smart door locks.
Considerations: Ensure compatibility with other smart devices and ease of setup. Voice activation can be especially useful for those with limited mobility.
Smart home technologies enhance safety by automating various home functions.
For example, smart lights can turn on automatically when motion is detected, reducing the risk of tripping in the dark, especially with motion sensors for elderly.
Voice-activated assistants can control lights, locks, and even call for help if needed.
Considerations for Selecting Fall Prevention Devices
When choosing fall prevention devices, it is important to consider the specific needs and lifestyle of the senior individual. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
1. Ease of Use: The device should be simple to use, with intuitive controls and easy-to-understand instructions.
2. Comfort: Wearable devices should be comfortable and non-intrusive to encourage regular use.
3. Reliability: Select devices from reputable manufacturers with good reviews and proven reliability.
4. Cost: Consider the cost of the device and any ongoing subscription fees for monitoring services. Check if any devices are covered by insurance.
5. Integration: Ensure the device can integrate with other safety systems and devices the senior may already be using.
6. Personalization: Look for devices that can be customized to meet the specific needs and preferences of the user.
Selecting the right fall prevention device involves evaluating various factors to ensure it meets the user's needs. Here are additional details to consider:
Battery Life: For wearable devices, battery life is crucial. Choose devices with long-lasting batteries to avoid frequent charging.
Range and Connectivity: For devices that rely on connectivity, such as PERS, ensure they have adequate range and reliable connectivity within the home or outdoors.
Maintenance: Consider the ease of maintaining the device. Devices that are easy to clean and maintain are more practical for everyday use.
Aesthetics: While functionality is paramount, the design and aesthetics of the device can also be important. Devices that look good and feel comfortable are more likely to be used consistently.
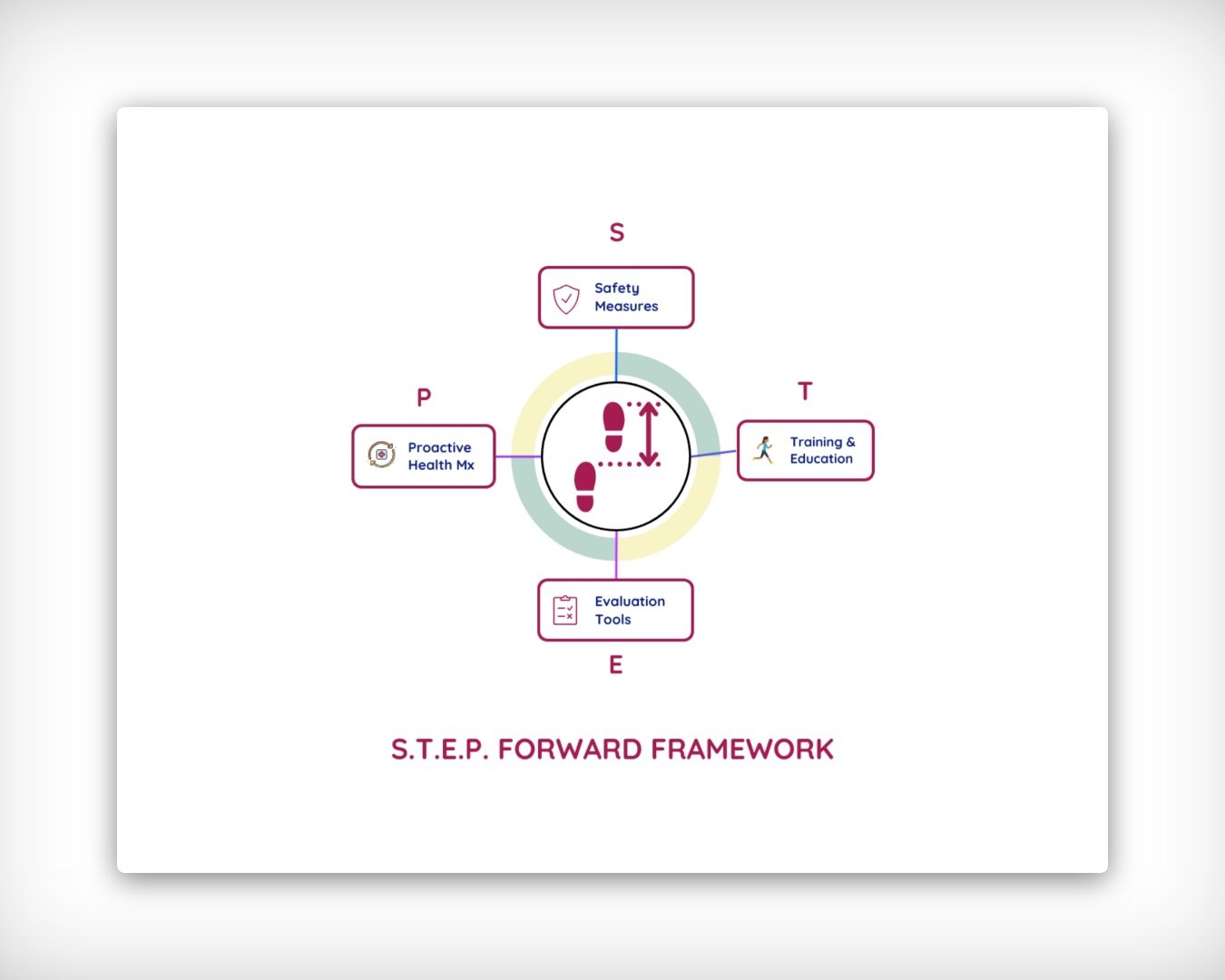
The Role of the S.T.E.P. Forward Method
The S.T.E.P. Forward Method incorporates these devices into a comprehensive fall prevention strategy.
By leveraging advanced technologies, the method ensures a holistic approach to enhancing safety and independence for seniors.
Key Components of the S.T.E.P. Forward Method:
1. Safety Measures: Implement home safety modifications and use assistive devices as needed.
2. Training and Education: Engage in tailored exercise programs and educational workshops on health and wellness.
3. Evaluation Tools: Utilize fall risk assessment tools, self-evaluation questionnaires, and physical function tests to track progress and adjust the program.
4. Proactive Health Management: Keep detailed logs of physical activity, nutrition, sleep, and emotional well-being.
By adopting the S.T.E.P. Forward Method, seniors can enjoy a structured and effective approach to fall prevention, enhancing their confidence and independence.
Examples of S.T.E.P. Forward Method Implementation:
Home Safety Assessments: Regularly review and update home safety measures to ensure a fall-proof environment.
Personalized Exercise Plans: Develop exercise routines tailored to individual abilities and needs.
Health Workshops: Participate in workshops that provide information on nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle modifications to support overall well-being, including fall prevention training.
Progress Tracking: Use logbooks to monitor daily activities, progress, and any changes in health status.
Conclusion
Fall prevention devices and technologies are vital tools in reducing the risk of falls among seniors. These fall assistance devices and anti-fall devices offer essential support.
From wearable sensors to smart home technologies, these devices offer increased safety, peace of mind, and support for independent living, including motion sensors for the elderly and fall monitoring systems.
When selecting fall prevention devices, consider the specific needs, ease of use, comfort, and reliability to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Next Step
Subscribe to Our App for Free
Join our Free Facebook Group
Download Our Movement Strategy Guide
For more information on the S.T.E.P. Forward Method and to begin your journey to a fall-free life:
Subscribe to our free iOS app to access the free mini-video series on Movement Strategies to Prevent Falls. If you're using a different device, access our web app from any device for the same great resources.
Join our free Facebook group, Fall-Free Wellness Circle, to connect with a community dedicated to safety and wellness.
Download our guide, "3 Movement Strategies for Seniors Who Want to Effortlessly Prevent Falls Without Heavy Equipment or Risky Exercises," to start implementing effective exercises today.
Every step counts when it comes to fall prevention—take yours now and embrace a safer, healthier future.